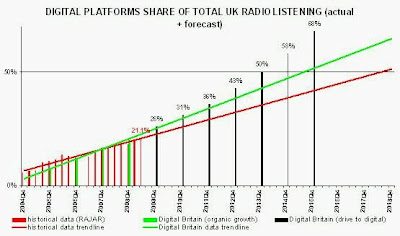
Q. Who will decide if/when digital radio switchover ever happens? The public. Who says so?
In July 2009, BBC ‘head of radio’ Tim Davie had said:
“… the idea that we would move to formally engaging [digital radio] switchover without talking to listeners, getting listener satisfaction numbers, all the various things we do, would be not our plan in any way.”
In August 2009, BBC Trust chairman Sir Michael Lyons had said:
“It is an extraordinarily ambitious suggestion, as colleagues have referred to, that by 2015 we will all be ready for [digital radio switchover]. So you can’t move faster than the British public want you to move on any issue.”
In July 2010, Culture Minister Ed Vaizey had said:
“If, and it is a big if, the consumer is ready, we will support a 2015 switchover date. But, as I have already said, it is the consumer, through their listening habits and purchasing decisions, who will ultimately determine the case for switchover.”
Q. What is the BBC’s strategy for digital radio switchover?
In July 2010, the BBC Trust told the BBC Executive that it:
“should draw up an overarching strategy for digital radio.”
Q. What is the public’s opinion of DAB radio?
Research published this week by the BBC Trust for the Strategy Review collated opinions voiced in 20 focus groups held in September 2010 in ten locations. Below are excerpts that relate consumers’ experiences with DAB radio and the BBC’s digital radio stations. They make sobering reading ….
 Key Findings
Key Findings
The availability of radio services on the move (especially in-car and for those working outdoors) was felt to be of continued high importance. People expect radio to stay portable – at least the range of stations they currently have available on analogue, including local stations which are critically important in-car for their local travel information. In this context especially there was strong resistance to the idea of analogue radio switch-off, and considerable scepticism as to whether or not this will actually happen.
4.2 The range of services provided by the BBC
“Rather than spending money on Radio 57 or whatever, invest more money on the core main programmes.”
35-44, Male, C2DE, Crowthorne
4.3 Attitudes to DAB radio
Many of the distribution issues we set out to discuss in the groups related to the availability of DAB (or of certain stations on DAB). However, what became clear in the groups was that, although we did speak to some real fans of DAB, most licence fee payers we spoke to do not yet view DAB as an essential service in the way they do Freeview, for example. This certainly coloured their reaction to some of the trade-offs they encountered between funding distribution and content.
“I think they should improve the Freeview signal before they start worrying about the radio. Radio is fine.”
18-24, Female, ABC1, Inverness
These attitudes were coloured by a number of factors:
· Limited awareness of what DAB is and what it offers
· Limited awareness and uptake of the BBC’s digital-only radio stations (most digital radio listeners within the groups were using digital radio as a means of listening to stations they would otherwise be able to receive via analogue)
· Most DAB set owners we spoke to had received them as presents – they hadn’t necessarily had a compelling reason to buy one
· Many trialists of DAB in the groups had been frustrated with their experiences – e.g. intermittent/non-existent signals, limited range of their favourite stations available
· Some doubts as to whether DAB technology will be around in the long term
“I did have a DAB radio but I didn’t notice it being any better”
18-24, Female, C2DE, Cheddar
“I find DAB radio can be quite troublesome although that’s not BBC specific. The signal seems to interrupt quite regularly”
45-59, Female, ABC1, Crowthorne
“I don’t find that DAB radio is achieving a lot for me. It’s supposed to be better quality, but because of the size of the set I’ve got, it doesn’t really make any difference.”
55+, C2DE, Derby
“Aren’t we the only ones to use DAB? Europe uses a different system and America too – I don’t see the point of it now so many people have the internet as it’s as cheap to get an internet radio as it is a DAB radio and you can listen to far more stations on it”
25-44, ABC1, Fort William
“You can’t get much [on DAB in the car] – no Radio 1, no Radio 2, no Radio 5 live, no Radio 4, you just get a message saying ‘no reception’. You need to be on top of a mountain to receive it. It’s a complete waste of time.”
55+, C2DE, Derby
There was real confusion and in some cases concern about the idea of a digital switchover for radio, and some debate as to whether the mooted date of 2015 was realistic or not. Certainly in the current circumstances there would be much resistance among participants in these groups to the idea of switching off analogue radio, especially those for whom in-car listening was an important (or the dominant) part of their radio listening.
“They can’t switch off analogue radio – people are really not going to be happy with that”
18-24, Male, C2DE, Belfast
“The idea of making all radios into digital is just ridiculous… It’s not persuading you – it’s just pushing you”
18-24, Female, C2DE, Cheddar
“What about all the car radios – surely we’re not going to replace all those?”
25-34, Female, ABC1, Caernarfon
“Are you telling me my radios will be totally obsolete if they do this? That’s outrageous”
60+, Female, ABC1, Newry
5.1 Availability of services
“I’m going to sound old fashioned but the core product is BBC One, BBC Two and Radios 1 to 5”
35-44, Male, C2DE, Crowthorne
The digital-only radio stations were considered of significantly lesser importance (awareness of these was limited, and listening to them was quite sporadic through the sample). In fact in several groups it was suggested that one solution to the complex problems of making access to digital radio more easily available to people would be to get rid of the stations altogether!
“I don’t think anyone really cares about the digital channels and they won’t until all the non-digital signals have been turned off”
25-34, Male, C2DE, Newry
“It’s limited because digital radio hasn’t really taken off.. they’re talking about changing over in 2015… if it’s half the hassle of the digital [TV] switchover, it will be a dead loss”
45-64, ABC1, Merthyr Tydfil
6.1 Availability of platform choice
There was also a general consensus across the groups that, although the convergence of platforms has started to offer useful additional means of consuming ‘broadcast’ services, as a minimum the BBC’s television services should be available via a television set, and the main radio services via a radio set.
“It’s good enough to be able to get main stations on analogue radio and the others through the TV – I don’t think they need to be able to get all these radio stations on radio only.”
25-34, Female, ABC1, Caernarfon
Lack of availability of BBC Radio Derby on DAB
Local radio was considered to fulfil an important community service, particularly by those in the older group, who remarked that there had been a decline in the range of local media available (local newspapers closing, and the ITV regional television coverage now being focused on Birmingham).
As such, BBC Radio Derby was felt to be important to giving the city a sense of identity. Sports coverage was an integral part of this (for the men especially), and Derby-specific coverage was felt to help ensure that they don’t live in the shadow of nearby Nottingham. Frequently, they felt, Derby is treated like a poor relation next to Nottingham; the availability of BBC Radio Nottingham (but not BBC Radio Derby) on DAB was yet another manifestation of this, they believed.
A number of them had bought DAB radio specifically with the intention of listening to BBC Radio Derby and had thus been extremely disappointed not to be able to find it.
“I asked for a DAB set for Christmas, specifically so I would be able to listen to Radio Derby, nice and clear, around the house – not realising that you can’t get Radio Derby on DAB at all… I only found out when I pressed the ‘auto-scan’ button… Leicester, Nottingham, loud and clear, but no Derby… I felt really let down.”
55+, C2DE, Derby
“My wife bought me one for Christmas. It wouldn’t work next to the bed – we thought it was broken. We ended up just using it as an alarm clock. It never occurred to me that it might not work depending on where you live.”
40-54, ABC1, Derby
There was little awareness or understanding of the reasons why this is the case (the lack of a local commercial multiplex operator), so some participants were upset that the BBC appeared to be viewing Derby as a lower priority than neighbouring areas. Others had assumed that this was a technical issue (reception problems), rather than the station not being broadcast on DAB. (There was some awareness of a promised launch date of July 2010, but they claimed that this date had been and gone with no further update on what was happening.)
“What makes me angry is that Radio Derby comes out as one of the best local news stations in the country, but it’s not available on the latest technology.”
55+, C2DE, Derby
“If you can get the others, you’d just assume that you can get Radio Derby as well. Whose decision is it not to have it?”
40-54, ABC1, Derby
Some of the participants had experimented with some of the BBC’s digital-only stations on DAB. Radio 7 in particular was well-liked by some of the participants in the older group, and some of the younger men had used 5 live Sports Extra, but their overall impression with DAB was one of disappointment. The absence of BBC Radio Derby was a significant contributor to this, along with poor reception quality.
“The way they sell DAB it was going to be the be-all-and-end-all of radio listening, but it’s just been a great disappointment.”
55+, C2DE, Derby
Although many were disappointed with DAB in general, the absence of BBC Radio Derby from DAB was not felt to be a major problem for them as long as the station remains available on analogue (many were listening out of home in any case – traffic reports in the car, or match commentary when out and about at the weekend).
However, in line with most other groups, these participants would be extremely upset if the analogue signal were switched off and BBC Derby only then available online.
Radio Foyle on DAB
Many participants felt that they get a better reception with DAB than on analogue (in the home). Many of the older group in particular claimed to have experienced reception problems with Radio Foyle in particular on analogue, especially in bad weather. However it was not a case of a having had a desperate need to get a digital radio because they got no analogue signal previously, more that the sound was not always great and they sometimes experienced reception problems.
“DAB radio… I got it out of curiosity… everybody said it was better than analogue… the analogue sometimes you can’t tune in because you have got high pressure or rain or wind. The DAB you can pick it up.”
50+, ABC1, Londonderry
Most assumed that Radio Foyle was already on DAB, as they insisted they were listening to it on their DAB radios – it is not entirely clear whether this is confusion between DAB and analogue signals on the same set, or they have been experiencing the ‘dynamuxing’ test.
“No I didn’t know that because when I press it comes up on my DAB radio so I thought it was. I just took it that all the stations I can pick up on my DAB are digital.”
50+, ABC1, Londonderry
“Foyle on an ordinary radio is still poor I think. I am right in Derry. On the digital they do both seem clear to me.”
30-49, C2DE, Londonderry
When it was explained to them that ‘dynamuxing’ the two stations would result in two mono (as opposed to one stereo) stations, reactions were somewhat mixed. Although some participants were adamant that going from stereo to mono would compromise their listening experience, particularly when listening to music, others admitted that they were not sure what mono sound is, and probably wouldn’t be able to tell the difference! It is also worth noting that, from the description they gave of their DAB sets, the majority of participants in the groups were listening to DAB on mono-only sets anyway.
On balance, all participants would prefer both stations to be available, even if this meant mono-only broadcasting. The younger group, who were more loyal Foyle listeners, were happy enough with the availability of Foyle on analogue only, but would be concerned by the prospect of an analogue radio switch-off, in which case continued availability of Foyle would be vital.
Poor DAB coverage (in Fort William)
Most of the participants in the groups are used to struggling with coverage issues. Lack of DAB coverage is just the latest manifestation of issues they have experienced historically with analogue television and radio signals.
“I live over in a rural area completely surrounded by hills so there is no radio reception at all so all our radio listening is done through the TV box or the internet”
25-44, ABC1, Fort William
“I tried a DAB radio but it wasn’t very good – it would go for a bit then completely cut out and we have no FM signal at all out in the glens where I am”
45-64, C2DE, Fort William
As a result, satellite (by which most really meant Sky, as awareness of Freesat was very low) had become the default standard for most to receive television, especially for those outside the main town of Fort William itself, and many were increasingly using the good broadband services that are now available to them as a more reliable means of accessing media content.
“We’ve been up there seven years now and when we first moved we had a reasonable medium wave signal for Radio Scotland but then that tailed off but we get no FM and there was no TV until satellite came on stream… We had very young children at the time and they were happy just watching DVDs… There are about 250 people in our village and many of the surrounding communities have the same issues… There used to be a mast for the TV but that was turned off and now everyone has a satellite dish… satellite has been a godsend for us – especially for the radio – but we are now even more likely to be listening online. Our broadband is excellent – 8Meg – and now we even have wi-fi radios in the house.”
25-44, ABC1, Fort William
Some participants in the groups had been drawn to DAB, but left frustrated by the experience.
“I won a DAB in a Radio Scotland competition and I was really excited about being able to listen to 6 Music but there was absolutely no signal so I gave it to my dad down in Glasgow and he’s really happy with it”
25-44, ABC1, Fort William
Limited availability of Radio Wales and Radio Cymru on DAB
In common with many of the research locations across the country, issues surrounding the lack of availability of Radio Wales and Radio Cymru were caught up in other issues around the quality of DAB signal in general.
While some participants (for example, one lived near a mast) were experiencing extremely good reception via digital, others were having problems based on their location and even the prevailing weather conditions.
“If you get a rain cloud overhead, or worse than that the snow, you might as well chuck it in the bin.”
45-64, ABC1, Merthyr Tydfil
“People who live in the dips – they can’t get any kind of digital radio reception at all… they’ve got to do something to help them.”
25-44, C2DE, Merthyr Tydfil
This frustration was a manifestation of a broader dissatisfaction with digital reception in general. Many were experiencing problems with their television reception (especially, but not exclusively through Freeview). Lack of a reliable television signal was seen by most as a more significant problem than lack of a reliable radio signal.
“They said the digital signal was going to be better – that you’d be able to get S4C and Channel 4 – but it’s actually worse.”
25-44, C2DE, Merthyr Tydfil
“Wales has always got problems, we get worse service with the digital, the broadband, the post… We pay the same, we have a right to the same service.”
25-44, C2DE, Merthyr Tydfil
As a result many in the groups considered themselves to be disgruntled licence fee payers.
Most could understand that there are diminishing returns in terms of building out the transmitter network, and that those in the more mountainous parts of central Wales (for example) might not be able to have access to the same choices as people in more densely populated areas. However, in these groups the argument was most strongly made that people in these areas should have some kind of discount from their licence fee in recognition of the reduced service they receive.
“They [the BBC] can’t please everyone, they’re doing the best they can, but If people can’t get the service, why should they pay the full money.”
45-64, ABC1, Merthyr Tydfil
“You shouldn’t be penalised for living in an area where they can’t provide these services, because we have to pay extra to get Sky, for example, to be able to receive it.”
45-64, ABC1, Merthyr Tydfil