The most startling suggestion in the recent report on “The Drive to Digital” commissioned by RadioCentre is the part that details the prerequisites for commercial radio to “forge ahead with DAB”:
“This requires changes to terms of trade and the active support of the other principal players in radio – the government, Ofcom, the BBC and Arqiva – including commitment not to pursue alternative technologies to DAB” [emphasis added].
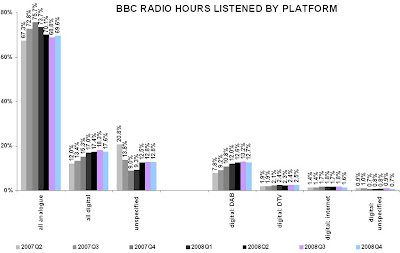
In other words, commercial radio considers that the way to make the DAB platform a successful technology is to force the remaining stakeholders – notably the BBC – to stop using other alternative digital delivery platforms (the internet, Freeview, Sky, FreeSat, mobile phones) to distribute radio. This would effectively force consumers who want to listen to, for example, digital station BBC7 to purchase DAB radios whereas, at present, the station can be received on the full range of digital platforms.
This sounds like an extreme solution to a challenging problem, beating consumers with a DAB ‘stick’. After almost a decade, the industry has had to reluctantly admit that its ‘carrot’ approach has failed to convince the public of the value of DAB radio. The RadioCentre report acknowledges that “[DAB] has been plagued by a damaging combination of slow take-up, poor coverage, high costs and uncompelling content” and that “there is not as much DAB-only material as hoped, and very little that’s truly compelling – there’s no ‘must have’ content as with sports & movies on Sky [TV]”.
The notion of forcing, rather than persuading, the public to use the DAB platform had been touched upon in the Final Report of the Digital Radio Working Group published in December 2008. It noted that “many of the consumer groups believe that, once an announcement [of an AM/FM switch-off date] is made, no equipment should be sold that does not deliver both DAB and FM”.
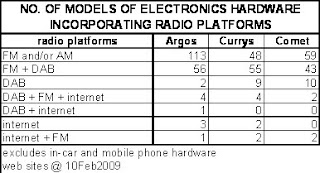
Such a proposal would prove impossible to put into practice. Most consumer electronics hardware is made by global companies whose models benefit from ‘universality’ and not from having to manufacture a special UK-only version that would incorporate the DAB platform. Right now, there is not a single mobile phone on sale in the UK that includes the DAB platform, and that situation is unlikely to change because Nokia, Samsung, Sony, LG and Motorola understandably consider FM radio to be the universal radio platform.
A similarly unrealistic proposal for DAB surfaced in March 2008, when Channel 4 Radio commissioned an independent report that proposed:
“to distribute one digital (DAB+) radio set [free of charge] to each household – approximately 26 million sets in total – to stimulate mass take up of digital radio. The sets would be provided over a period of three years, starting in 2010, with 80% distributed over the first two. The total cost of the ‘switch-on’ plan (DAB+ sets, marketing campaign and administration) would be £383m […]. Preliminary thinking is that distribution would use vouchers that would be redeemed in larger retail outlets or via promotional codes online”.
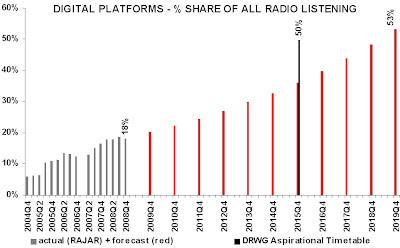
The report anticipated that such a mass consumer giveaway “could result in 60% digital listening by 2012” whereas, without it, “digital listening may not reach 60% until 2017, with analogue switch-off no earlier than 2020”. However, the hypothesis failed to consider that a household given a free DAB radio might not necessarily use it, if there were no radio content of sufficient appeal broadcast on the platform. Given that the average household has six radio receivers, a free distribution such as this might simply result in a glut of unused DAB receivers advertised on E-bay.
Such unrealistic proposals only serve to demonstrate a phenomenon highlighted by a web site that is currently nominating DAB radio for the ‘Fiasco Award 2009’ in Spain:
“The fact that a technology is possible does not necessarily mean that people is willing to pay for it, and the fact that Institutions and Companies support it does not mean they did the necessary previous research: they were probably just thinking that they didn’t want to be left behind.”
In the case of the DAB platform, its forced take-up would be the last opportunity remaining for the largest UK commercial radio owners to throw a protectionist cloak around their assets. Through their joint ownership of the DAB platform infrastructure in the UK, this handful of companies hope to limit UK citizens’ future radio listening to their content broadcast on their stations received via their DAB platform. To make this scenario work, of course it would be essential to eradicate competing digital radio platforms.
And why are radio owners so desperate? An excellent US article this week by Seeking Alpha’s Jeff Jarvis expressed the reasons most eloquently:
“We’ve been wringing hands over newspapers and magazines, but TV and radio aren’t far behind. Broadcast is next. It’s a failure of distribution as a business model. Distribution is a scarcity business: ‘I control the tower/press/wire and you don’t and that’s what makes my business.’ Not long ago, they said that owning these channels was tantamount to owning a mint. No more. The same was said of content. But it’s relationships (read: links) that create value today. Young [Broadcasting, filing for bankruptcy with $1bn debt] tried to build relationships, once upon a time. At WKRN in Nashville, Mike Sechrist did amazing work starting blogs, building relationships with bloggers, training the community in the skills of the TV priesthood. But he left and all that disappeared. Been there, done that, I can imagine executives saying as they try to stuff the hole in the dike with borrowed dollars. Didn’t work. The local TV and radio business, once a privilege to be part of, is next to fall. Timber.”
As if that was not enough, the credit crunch has exposed the flimsy financial arrangements of recent radio acquisition deals. This was perfectly explained by Jerry Del Colliano’s consistently provocative US blog in an entry entitled ‘Radio: bankrupt in 6 to 12 months’:
“Consolidated radio groups are facing bankruptcy because some will not be able to restructure their massive debt — the debt they acquired in the first place when they paid too much for overvalued radio stations. No one worried about it then. But now, it’s time to pay the piper. Why else do you think radio people who know better are hunkering down for what they know is coming — default.”
“One reader, a radio executive, claims New York money types are not just talking about the possibility of radio groups defaulting, but the probability. Some think it can happen within six months to a year. Radio groups like Cumulus, Univision, Clear Channel, Entercom — in fact, most of them — have structures that make it difficult to survive if debt cannot be restructured. And in case you haven’t noticed, money is hard to come by these days…….”
“Radio groups are more susceptible because they are leveraged to such a high degree. That’s the reason that the stock prices are so low. Shareholder equity is zero as every single penny of cash flow currently goes to servicing debt. Soon, they won’t be able to service the debt and/or they will be in violation of covenants with the banks and/or equity lenders who will seek to take the stations back.”
If this sounds like cross-Atlantic doom-mongering, I assure you that there are UK banks out there already demanding their pound of flesh from more than one indebted UK radio group. 2009 will not be a pretty year. Particularly when Quarter 4 2008 UK radio revenues were down 15% year-on-year, their lowest quarter since 1999.
In these troubled times, proposing radio sector policies to preserve broadcasters’ oligopolies, or to artificially stifle the development of competing delivery platforms, is not what is needed. Sure, you might wish to be the only ship on the ocean but, if your rust bucket has a hole in its hull, you will drown anyway.
[thanks to The Guardian’s Jack Schofield]


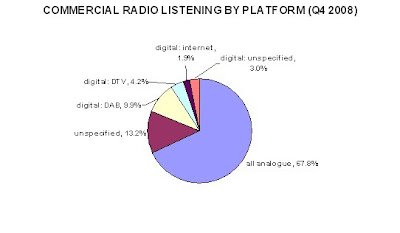
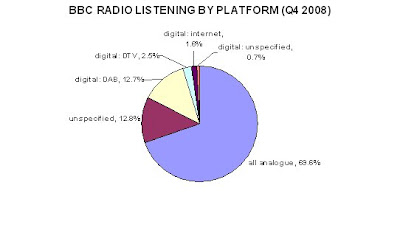





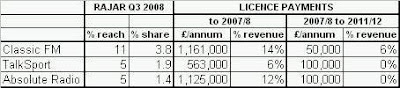
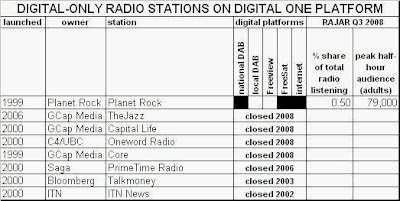 It hardly inspires confidence in the Digital One DAB platform that Global Radio’s predecessor, GCap Media, closed three of its own digital-only stations carried on its platform last year, and sold Planet Rock to an entrepreneur with no other radio interests. Neither is it a good advertisement for Digital One that its
It hardly inspires confidence in the Digital One DAB platform that Global Radio’s predecessor, GCap Media, closed three of its own digital-only stations carried on its platform last year, and sold Planet Rock to an entrepreneur with no other radio interests. Neither is it a good advertisement for Digital One that its