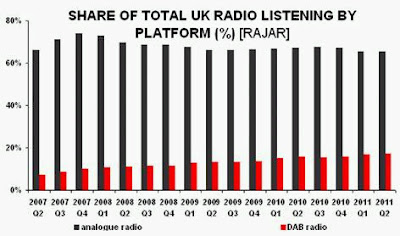
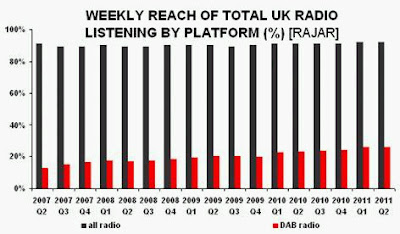
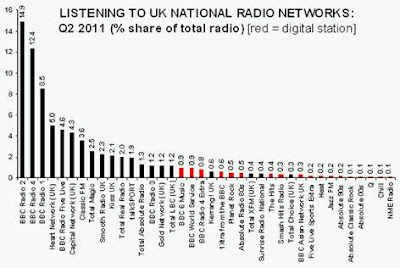
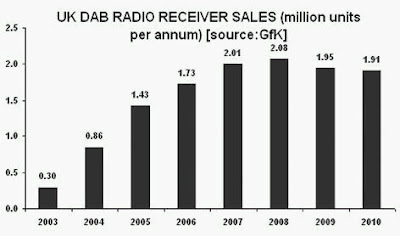
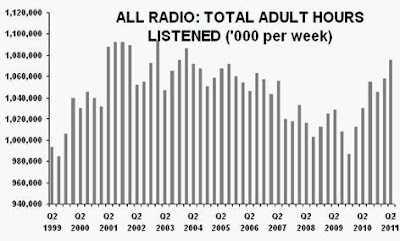
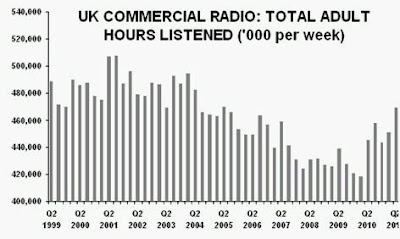
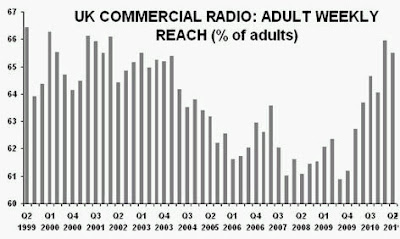
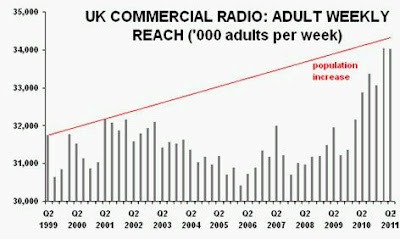
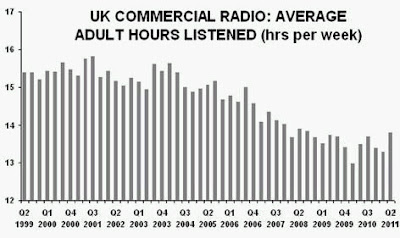
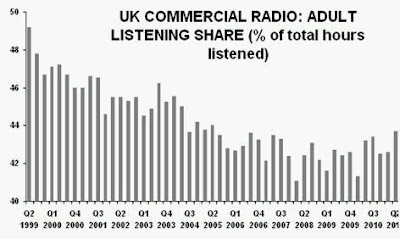
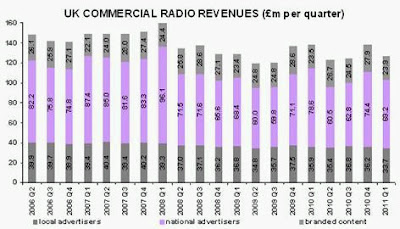
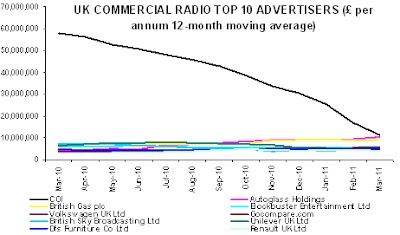
“Without a knowledge of your history, you cannot determine your destiny” Misty In Roots, ‘Live At The Counter-Eurovision 1979’
I love history. I hated History. My Empire-made History GCE text book chronicled world history from the era Neanderthal Man emerged from Milton Keynes up to Britain’s singlehanded success winning the Second World War. Neither the book nor my teacher brought history to life, debated the outcomes or analysed lessons learned. Weekly homework was an essay merely paraphrasing one chapter of the book. Termly tests required regurgitation of these essays, a task I failed as I could not memorise names, dates and events by rote. After two tortuous years, we had just learned of Hannibal opening an elephant sanctuary and Britain’s offer to the Romans of work visas to build its roads and public baths … when I was finally allowed to drop History.
Before grammar school beat History out of me, I had developed my own random interest in the subject. We had few books in our home and my parents had a remarkably hands-off attitude to childrearing, so the local library substituted as my mentor as soon as I could walk. I would stagger along the 500-metre route home weighed down with dozens of fiction and non-fiction books, my borrowing limit enhanced hugely by additional tickets I had registered in the names of my younger brother, parents and grandparents. Junior school set no homework, my schoolfriends all lived a mile away and my parents left me home alone most weekends to build their dream house, so I read voraciously. Combining the librarians’ helpful suggestions with my own casual curiosity, I devoured The Narnia Chronicles by age eight, lost interest in finishing ‘The Lord of The Rings’ at age nine and was given nightmares by John Fowles’ novels at age ten.
Radio broadcasting had emerged as an early interest, stimulated by my parents’ love of ‘Big L’ on their car radio, so I collected any information I found about the industry, clipping news stories from newspapers and Pritt sticking them into scrapbooks. Much later, I combed second-hand book sellers and charity shops for books to add to my growing personal collection. As one of Amazon’s earliest international customers, I had to fax a scan of my credit card to order arcane radio books unseen in Britain. I kept two lists, one of radio books I owned and the other of book titles I wanted, updated by scanning British Books in Print catalogues in libraries. I felt there was much I could learn about radio from its history.
It was not until the 1980’s that I discovered the library of the Independent Broadcasting Authority (IBA) government quango, a little-known haven in its Brompton Road office. Its diligent librarian clipped every story about broadcasting from national and local newspapers and filed them by topic in folders. I spent weeks there, probably months in total, reading commercial radio licence applications and researching the history of commercial radio from its launch in 1973. Cuttings in the library’s ‘pirate radio’ folders proved an essential source for my narrative about the two-decade struggle by London pirate stations for legal status published later in my KISS FM book. Then, in 1991, the government split the IBA into separate regulators for television and radio. The library that had proven so invaluable suddenly vanished.
Years passed until I was reminded of the usefulness of this library when I was researching a report for the BBC Trust. Where was it now? I learnt that it had been stuffed into 1,100 boxes containing a million documents and been donated to Bournemouth University. However, 800 of those boxes remained archived in an off-site storage facility that could not be visited. The University sent me a 10MB file of its ‘IBA Archive’ that detailed its contents, but it had been compiled in Microsoft Access, not a software within reach of a cheapskate non-academic. Dead end. My cherished memories of reading thousands of documents in the air-conditioned comfort of the peaceful IBA library would never be repeated.
The government replaced the IBA with The Radio Authority for the regulation of commercial radio. In 2002, on my first day of employment there in a junior role, I was shown around all the offices of its floor within a Holborn tower block. At the end of the tour, I asked: “Where is the library?”
“Library?”, my guide laughed. “We don’t have a library.” I was nonplussed.
“But you receive hundreds of applications for radio licences,” I replied. “What happens to them?” A decade earlier, I had sat in the IBA library for days reading dozens of radio licence applications. Then I had written the application for London pirate station KISS FM that had won its licence. I knew from experience that applications could be as thick as phone directories and included detailed tables, spreadsheets, budgets, programme plans and market research. They were significant historical documents.
“Once we have read the applications and awarded a particular licence, we send them to an archive somewhere,” replied my guide. “If you want a particular document, you CAN request it. But it can take weeks or months to be delivered from the archive.” I was still reeling. I was thinking to myself: surely the basic day-to-day task of a media regulator is to ensure that a radio station acts upon the promises that it has made in its licence application. But if that document is not at hand, apparently not.
By the end of my first day of work, this conversation was just the first indication of baffling work practises I encountered at The Radio Authority. One year later, the organisation was preparing to be closed and merged into a new regulator named Ofcom. Each of the forty-odd staff was required to join an assigned group that was preparing the merger. I was told to attend meetings of an Ofcom sub-sub-subcommittee that I found had no responsibility for radio. My contribution was nil.
Then, unexpectedly, one of the managers approached me and assigned me a second task. The entire correspondence between commercial radio stations and the IBA, plus its successor The Radio Authority, was kept in a series of packed filing cabinets in the finance office, ordered by sequential chronological licence number. These were effectively the regulator’s master files. Nothing at the organisation was stored digitally. Everything was still on paper.
What was my new task? I was ordered to look at the paperwork of every licenced radio station and destroy all documents that were not a legal or contractual requirement. Day-to-day correspondence in both directions would be discarded. I was told that Ofcom had requested the records of commercial radio licences be reduced from several overflowing filing cabinets to a single drawer. Everything not legally required had to be destroyed. (Afterwards I was uncertain if this had been a genuine Ofcom order or just a useful excuse to destroy evidence.)
I was conflicted. To this day, I fail to comprehend whether I was given this task because I had a better knowledge of radio history than my colleagues (only one other of whom had worked in a commercial radio station). Or was it an act of deliberate cruelty by a manager who had already screamed at me for having had the temerity to write and circulate documents that analysed the radio industry WITHOUT HAVING BEEN ORDERED TO? Was I being valued … or bullied?
I set to work over the following weeks, glancing at each report and item of correspondence filed during the thirty-year history of Britain’s 267 commercial radio stations. The only exception was KISS FM’s folder which I had been forbidden to handle. I had to discard more than ninety percent of this fascinating history. Other staff were similarly throwing out their own paper records, filling huge fabric sacks that lined both sides of the main corridor. At times the volume of rubbish was so great that it became difficult to navigate until the weekly pick-up. The scene resembled a movie thriller when the bad guys have been tipped about an imminent police raid and then rush hell for leather to destroy all their incriminating evidence. During those few months, we produced dozens of rubbish bags that were to be shredded and burnt.
I was sorely tempted to try and save some of these historical documents but, having signed some kind of Official Secrets Act on my first day of work, I realised I could be prosecuted if any of these discarded documents ever appeared in public. For consolation, I salvaged the contents of the stationery room which bizarrely had also been binned, hid it all under my desk and took home night-by-night sufficient paper, pens, notepads and folders to supply my household for the next decade. Many of The Radio Authority’s senior staff had chosen to retire rather than transfer to the new regulator, so we can only guess how many skeletons in their office closets were burned in the organisation’s bonfire of the vanities.
After decades having researched, read and created a personal library focused on the history of radio broadcasting, it remains difficult to reconcile this crazed episode in my career when I had to incinerate a significant part of that history. I love history. I hated being ordered to destroy so much irreplaceable history at The Radio Authority. Having worked in Germany and Cambodia, I know what horrors sometimes follow such book burnings.
[Originally published at https://peoplelikeyoudontworkinradio.blogspot.com/2023/02/the-fahrenheit-451-of-commercial-radio.html]